Systems for managing sales are crucial resources for companies looking to streamline, monitor, and enhance their sales procedures. In today’s cutthroat business environment, when properly managing sales and customer relations may have a big impact on a company’s bottom line, these systems have grown in significance.
Definition and purpose

A sales management system is a software solution designed to help sales teams and managers handle various aspects of the sales process. Its main objective is to offer a single platform for tracking sales prospects, managing client data, estimating revenue, and evaluating performance indicators. Businesses can improve control over their sales operations and make more informed decisions by combining these features into a single system.
These systems serve multiple purposes:
- Centralizing customer and prospect data
- Automating repetitive tasks
- Providing real-time insights into sales performance
- Facilitating communication between team members
- Standardizing sales processes across the organization
Evolution of sales management technology
The concept of sales management has been around for decades, but the technology supporting it has evolved significantly. Sales teams used to keep track of their actions and customer data manually using spreadsheets, paper files, and simple contact management software. But when companies expanded and got more intricate, the need for more sophisticated tools became apparent.
The advent of customer relationship management (CRM) systems in the 1990s marked a significant milestone in the evolution of sales management technology. These technologies offered a more thorough method of overseeing sales procedures and consumer contacts. Cloud computing and mobile devices further changed the scene as technology developed, allowing sales teams to access and update information at any time and from any location.
Key milestones in the evolution of sales management technology include:
- 1980s: Introduction of database management systems
- 1990s: Rise of customer relationship management (CRM) software
- 2000s: Emergence of cloud-based solutions
- 2010s: Integration of social media and mobile technologies
- 2020s: Incorporation of AI and machine learning capabilities
Today, modern sales management systems incorporate advanced features such as artificial intelligence, predictive analytics, and integration with other business tools, making them more powerful and useful than ever before. These systems continue to evolve, adapting to changing business needs and technological advancements.
2. Key Components of a Sales Management System
A robust sales management system typically includes several core components that work together to support various aspects of the sales process. Let’s explore these key components in detail:
Customer and lead management
This component focuses on organizing and managing information about customers and potential leads. It typically includes features such as:
- Contact information storage: Centralized database for storing and accessing customer and lead contact details.
- Interaction history tracking: Recording of all customer interactions, including emails, phone calls, and meetings.
- Lead scoring and qualification: Automated system for ranking leads based on their likelihood to convert.
- Customer segmentation: Ability to group customers based on various criteria for targeted marketing and sales efforts.
Additionally, this component often includes:
- Social media integration for gathering additional customer insights
- Automated data enrichment to keep customer information up-to-date
- Custom fields for industry-specific information
Pipeline and opportunity tracking
The pipeline and opportunity tracking component helps sales teams manage their deals from initial contact to closure. Key features include:
- Visual representation of the sales pipeline: Graphical display of all ongoing deals and their current stages.
- Deal stage tracking: Ability to move deals through predefined stages of the sales process.
- Probability of closing estimates: Automatic or manual assignment of closing probabilities for each deal.
- Activity logging and reminders: Tools for recording actions taken and setting follow-up reminders.
This component may also offer:
- Customizable pipeline stages to match specific sales processes
- Automated stage progression based on predefined criteria
- Pipeline analysis tools to identify bottlenecks and opportunities for improvement
Sales forecasting and analytics
This component utilizes data from various sources to provide insights and predictions about future sales performance. It often includes:
- Revenue forecasting tools: Algorithms that predict future sales based on historical data and current pipeline.
- Performance trend analysis: Tools for identifying patterns and trends in sales performance over time.
- Win/loss analysis: Features for examining successful and unsuccessful deals to improve future performance.
- Custom report generation: Ability to create tailored reports for different stakeholders and purposes.
Advanced systems might also offer:
- AI-powered predictive analytics for more accurate forecasting
- What-if scenario modeling to test different sales strategies
- Real-time dashboards for instant performance insights
Performance management and reporting
The performance management and reporting component helps sales managers track and evaluate the performance of their team members. Features may include:
- Individual and team performance metrics: Key performance indicators (KPIs) for measuring sales effectiveness.
- Goal setting and tracking: Tools for establishing and monitoring progress towards sales targets.
- Commission calculation: Automated systems for calculating sales commissions based on performance.
- Performance dashboards: Visual displays of key metrics for quick performance assessment.
Additional features might include:
- Gamification elements to motivate sales teams
- Peer comparison tools for fostering healthy competition
- Integration with HR systems for comprehensive performance management
Territory management
For businesses with geographically dispersed sales teams, territory management is crucial. This component typically offers:
- Geographic territory assignment: Tools for defining and assigning sales territories.
- Account distribution: Features for fairly distributing accounts among sales team members.
- Territory performance analysis: Metrics and reports for evaluating the performance of different territories.
- Quota management by territory: Ability to set and track quotas for each defined territory.
Advanced territory management features might include:
- AI-powered territory optimization suggestions
- Dynamic territory reassignment based on performance data
- Integration with mapping software for visual territory management
Quotation and proposal management
This component assists sales teams in creating and managing quotes and proposals for potential customers. Features often include:
- Quote generation tools: Templates and automation for creating professional quotes.
- Proposal templates: Customizable templates for creating compelling sales proposals.
- Approval workflows: Processes for reviewing and approving quotes and proposals.
- E-signature capabilities: Integration with electronic signature tools for faster deal closure.
Additional features may include:
- Integration with product catalogs and pricing databases
- Version control for tracking changes to quotes and proposals
- Analytics on proposal effectiveness and win rates
3. Types of Sales Management Systems
There are several types of sales management systems available in the market, each catering to different business needs and preferences. Here are the main categories:
CRM-based sales management
Many businesses choose to use customer relationship management (CRM) systems with built-in sales management features. These systems offer a unified platform for managing both customer relationships and sales processes. Popular examples include Salesforce, HubSpot, and Microsoft Dynamics.
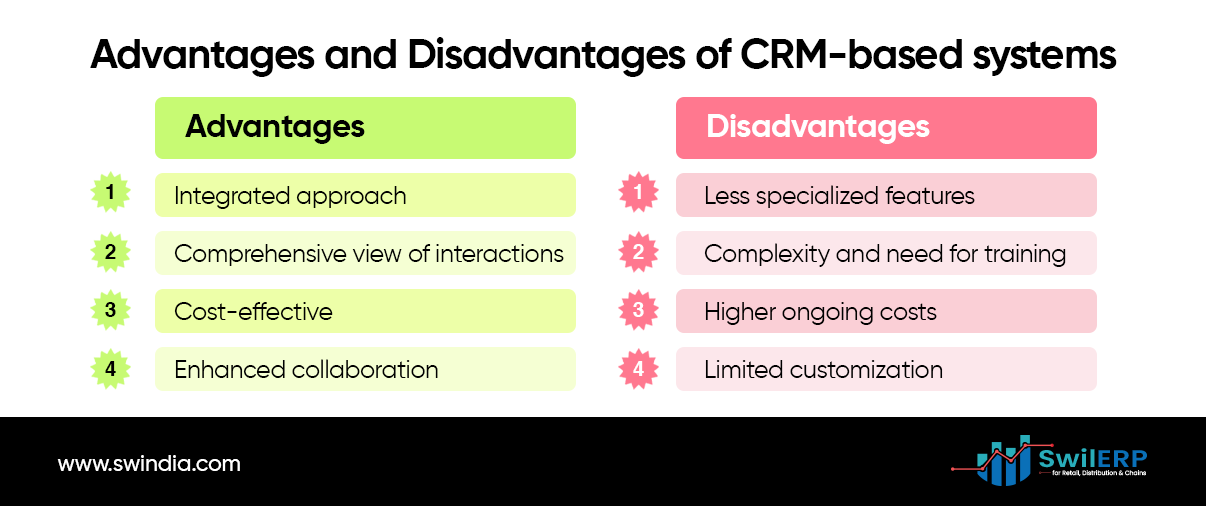
Advantages of CRM-based systems:
- Integrated approach to customer relationship and sales management
- A comprehensive view of customer interactions across departments
- Often more cost-effective than purchasing separate systems
- Enhanced collaboration and communication within the sales team.
Disadvantages:
- May have less specialized sales features compared to standalone solutions.
- Can be complex and require significant training for full utilization.
- Potentially higher ongoing costs for subscription and additional modules.
- Limited customization options due to standardized features.
Standalone sales management solutions
Some companies prefer dedicated sales management tools that focus specifically on sales-related functions. These solutions often provide more specialized features for sales teams but may require integration with other systems for complete functionality.
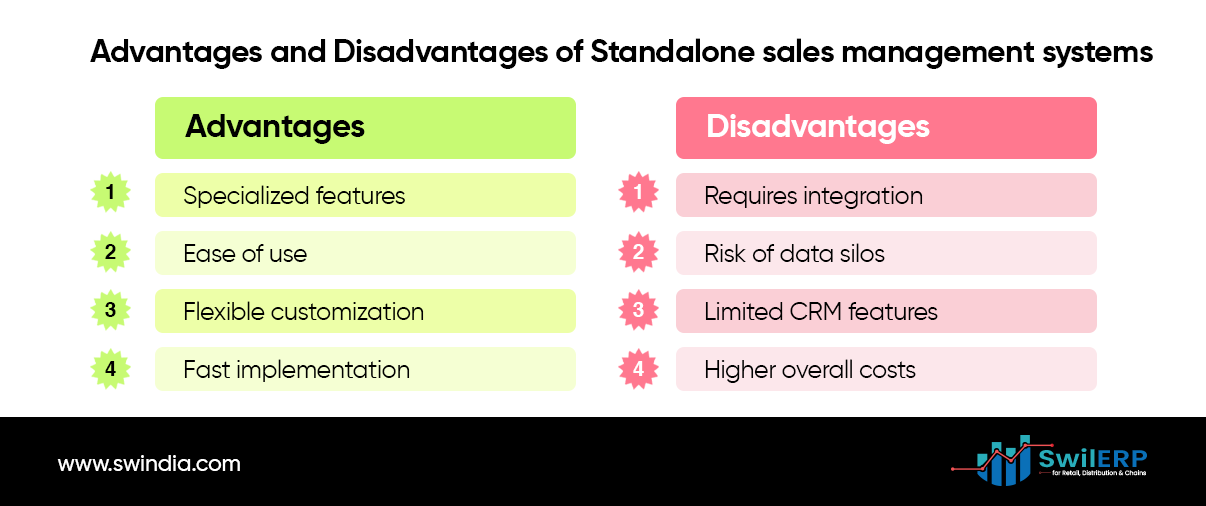
Advantages of stand-alone solutions:
- More focused and specialized sales features
- Often easier to use for sales teams
- Can be more flexible and easier to customize
- Typically faster implementation and adoption by sales teams
Disadvantages:
- May require integration with other systems for full functionality
- Potential for data silos if not properly integrated
- Limited features for customer relationship management compared to CRM systems.
- Higher overall costs when combined with other necessary systems.
Industry-specific systems
Certain industries have unique sales processes and requirements. As a result, some vendors offer sales management systems tailored to specific sectors such as real estate, pharmaceuticals, or manufacturing. These systems often include industry-specific terminology and workflows.
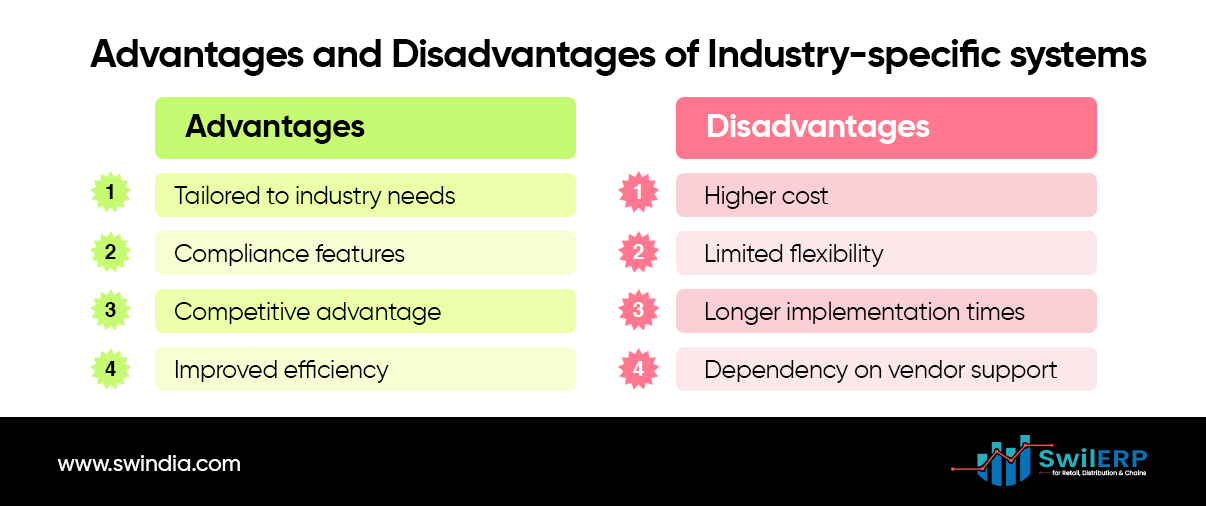
Advantages of industry-specific systems:
- Tailored to the unique needs and processes of specific industries
- Often include industry-specific compliance and regulatory features
- Can provide a competitive advantage through specialized functionality
- Improved efficiency and effectiveness in industry-specific tasks.
Disadvantages:
- May be more expensive than general-purpose solutions
- Limited flexibility if the business needs to change or diversify
- Potentially longer implementation times due to customization requirements.
- Higher dependency on the vendor for updates and support.
Cloud-based vs. on-premise solutions
Sales management systems can be deployed either in the cloud or on-premise:
Cloud-based solutions:
These are hosted on remote servers and accessed via the Internet. They offer flexibility, scalability, and lower upfront costs.
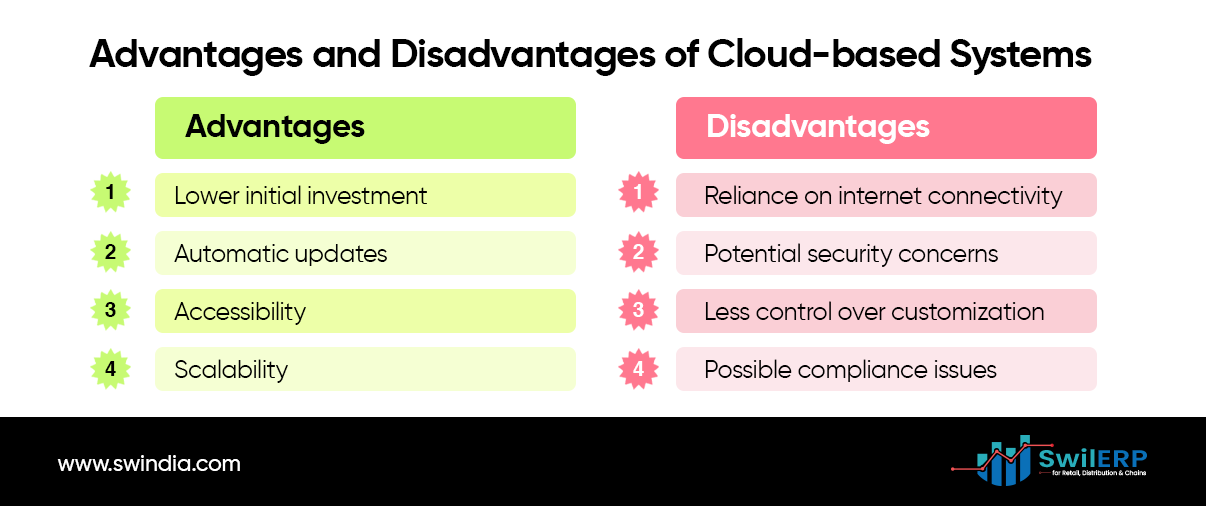
Advantages:
- Lower initial investment and predictable ongoing costs
- Automatic updates and maintenance
- Accessibility from anywhere with an internet connection
- Easy scalability as the business grows
Disadvantages:
- Reliance on internet connectivity
- Potential security concerns with data stored off-site
- Less control over data and customization options
- Possible data compliance issues depending on the industry.
On-premise solutions:
These are installed and run on the company’s servers. They provide more control over data and customization but often require higher initial investment and ongoing maintenance.
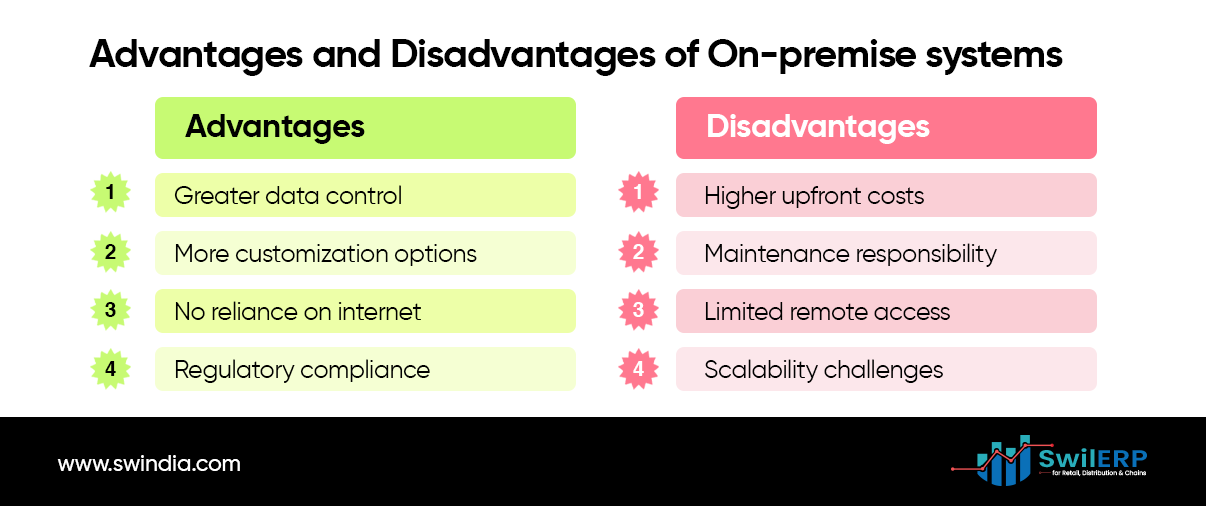
Advantages:
- Greater control over data and security
- More customization options
- No reliance on internet connectivity for access
- May be preferred for regulatory compliance in certain industries
Disadvantages:
- Higher upfront costs and ongoing maintenance expenses
- Responsibility for updates and security falls on the company
- Limited accessibility for remote workers
- Can be more difficult to scale
4. Benefits of Implementing a Sales Management System
Implementing a sales management system can bring numerous advantages to a business. Here are some key benefits:
Improved sales productivity and efficiency
A well-implemented sales management system can help sales teams work more productively by automating routine tasks, providing quick access to relevant information, and reducing administrative burdens. This allows sales representatives to focus more on selling and less on paperwork.
Specific productivity improvements include:
- Automated data entry and update processes
- Quick access to customer information and interaction history
- Automated reminders and task management
- Standardized sales processes and workflows
Enhanced visibility into the sales pipeline
With a centralized system for tracking deals and opportunities, sales managers can gain a clear view of their team’s pipeline. This visibility allows for better resource allocation and more accurate forecasting.
Benefits of improved pipeline visibility:
- Real-time overview of all ongoing deals
- Ability to identify bottlenecks in the sales process
- More accurate sales forecasting
- Better allocation of resources to high-potential opportunities
Better forecasting and decision-making
By leveraging data from various sources, sales management systems can provide more accurate sales forecasts. This information helps managers make informed decisions about strategy, resource allocation, and goal setting.
Improved decision-making capabilities:
- Data-driven insights into sales trends and patterns
- More accurate revenue projections
- Ability to identify and replicate successful sales strategies
- Early warning signs for potential issues or opportunities
Simplified sales processes
Sales management systems can help standardize and simplify sales processes across an organization. This standardization can lead to more consistent customer experiences and easier onboarding for new team members.
Benefits of simplified processes:
- Reduced errors and inconsistencies in sales activities
- Faster onboarding and training of new sales team members
- More consistent customer experience across different sales representatives
- Easier identification and replication of best practices
Improved team collaboration
Many sales management systems include features that facilitate better communication and collaboration among team members. This can lead to more effective knowledge sharing and improved overall team performance.
Collaboration benefits:
- Centralized communication platform for sales teams
- Ability to share best practices and successful strategies
- Improved coordination between sales, marketing, and customer service teams
- Enhanced mentoring and coaching opportunities
Data-driven sales strategies
With access to comprehensive data and analytics, sales teams can develop more effective, data-driven strategies. This approach can lead to better targeting of prospects, more personalized customer interactions, and ultimately, higher conversion rates.
Advantages of data-driven strategies:
- More targeted and personalized sales approaches
- Ability to identify and focus on high-value opportunities
- Continuous improvement based on performance data
- More effective allocation of marketing and sales resources
5. Choosing the Right Sales Management System
Selecting the appropriate sales management system for your organization is crucial for ensuring its successful adoption and use. Here are some key factors to consider:
Assessing organizational needs
Before evaluating different systems, it’s important to clearly define your organization’s specific requirements. Consider factors such as:
- Size of your sales team: Different systems are designed for different team sizes, from small businesses to enterprise-level organizations.
- Complexity of your sales process: Some industries or businesses have more complex sales cycles that require specialized features.
- Types of data you need to track: Consider what customer and sales data is most important for your business.
- Reporting and analysis needs: Determine what kinds of reports and analytics will be most valuable for your team.
- Budget constraints: Consider both upfront costs and ongoing expenses associated with the system.
Additional considerations:
- Current pain points in your sales process
- Future growth plans and how they might affect your needs
- Regulatory requirements specific to your industry
Scalability and customization options
As your business grows and evolves, your sales management needs may change. Look for a system that can scale with your organization and offer customization options to adapt to your unique processes.
Key scalability and customization features to consider:
- Ability to add users and functionality as your team grows
- Customizable fields and data structures
- Flexible workflow and process management tools
- API access for integration with other systems
- Options for creating custom reports and dashboards
Integration capabilities
Consider how well the sales management system can integrate with your existing tools and technologies, such as marketing automation platforms, accounting software, or customer support systems.
Important integrations to consider:
- Email and calendar systems
- Marketing automation tools
- Customer service and support platforms
- ERP and accounting systems
- E-commerce platforms
- Social media management tools
User experience and adoption considerations
The success of a sales management system largely depends on user adoption. Look for a system with an intuitive interface and user-friendly features that will encourage your team to use it consistently.
User experience factors to evaluate:
- Intuitive navigation and layout
- Customizable dashboards for different user roles
- Mobile app functionality and user experience
- Availability of training resources and user support
- Ease of data entry and retrieval
Mobile and remote access features
In today’s mobile-first world, it’s crucial to choose a system that offers robust mobile access. This allows your sales team to update information and access critical data while on the go.
Key mobile features to look for:
- Native mobile apps for iOS and Android
- Offline access to key data and features
- Mobile-optimized interface for easy use on smaller screens
- Push notifications for important updates or tasks
- Mobile data capture tools (e.g., business card scanning)
By carefully considering these factors and aligning them with your organization’s specific needs, you can select a sales management system that will provide long-term value and support your sales team’s success.



