E-invoicing involves the standardization of invoice reporting in India. E-invoicing is a system that facilitates convenience to taxpayers by simplifying the GST return system.
Taxation is always an integral part of the economy of any country. Thus, businesses have a responsibility to file their taxes on time and be up-to-date with new amendments.
Now, for any retail/wholesale business, it is necessary to revolutionize the business through advanced accounting and reporting systems for GST return filing and E-invoice generation.
In this blog, I am going to explain the important things that help you understand the full value of e-invoices in business step-by-step.
Know more on how to choose the right E-Invoice Solution.
Latest Updates –
December 26, 2022
As of 1st January 2023, there is no proposal before the GST Council and no plan for the government to implement the next phase of e-invoicing for businesses with turnover over Rs.5 crore.
October 11, 2022
GST Council may implement e-invoicing for businesses with an annual turnover of over Rs.5 crore from August 1st, 2023. The system may be expanded to companies with a turnover of over Rs.1 crore by the end of the next fiscal year.
August 1, 2022
By notice no. 17/2022, the e-Invoicing system for B2B transactions has now been expanded to those with an annual aggregate turnover of more than Rs. 10 crore up to Rs. 20 crore as of October 1, 2022.
February 24, 2022
According to notification number 1/2022, the e-Invoicing system will be made available to businesses with an annual aggregate revenue of more than Rs. 20 crore and up to Rs. 50 crore as of April 1, 2022.
Article Content-
- What is GST E-Invoicing System?
- What is the process of getting a GST e-invoice?
- Applicability of GST E-invoice System
- For Whom E-invoicing is Not Applicable?
- What are the consequences of forgetting to generate e-invoices?
- Features of e-invoice system you need to know
- Documents to be communicated under e-invoicing
- E-invoicing Template Mandatory Fields January 1, 2020
- Mandatory e-invoicing format fields with a due date of July 30, 2020
- Laser E-Invoice Bill Format with QR Code
- Benefits of e-invoicing system
- Generating e-invoices will impact the business processes as follows
- Businesses will get benefit from e-invoices in the following ways
- Details of the official website for e-invoice generation
- How will the e-invoicing system help businesses in the long run under GST?
- Role of e-invoicing in small, medium, and big enterprises
- SWIL GST Solution: Easiest Software Option to Handle E-Invoice
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Wrapping Up
What is the GST E-Invoicing System?
Traditionally, invoices were and are being manually done with a paper-based process. It has a greater potential for human error, increasing costs and processing company life cycles.
Over time, e-invoice has been implemented using technology. The e-invoice has an integrated electronic format that helps buyers and suppliers exchange their invoice documents electronically. It is designed to help companies that fall under the category of e-invoicing to file GST.
The concept of the GST e-invoice generation system has been designed keeping in mind the reduction in GST deception. It fixes issues related to fake invoices, fraud, and tax leakage, disturbing the entire taxation system.
It is an electronic invoicing system where an identification number is allocated for each B2B invoice by the invoice registration portal, which is looked after by the GST network (GSTIN).
This e-invoice system has a facility to update the invoice information in real-time for both GST and the e-way bill portal.
What is the process of getting a GST e-invoice?
The workflow of an e-invoice system can be classified into two parts. The first is the interaction between the business (for invoicing) and the Invoice registration portal (IRP). The second part is the interaction between IRP and GST / e-way bill system and buyer. It is necessary to know that you need to upgrade your system to make your business compliant with GST.
For this, the taxpayer or business need to create invoices and then need to submit them to the Invoice Registration Portal (IRP) for approval. After successful verification, the portal will return the invoice to the supplier with a unique reference number, digital signature, and a QR code.
Also, the generated e-invoice will be shared with the respective buyer on the provided email ID. So, the following steps are needed to be followed to generate it on the GST e-invoice portal.
Process 1: Invoice Creation
This is the first step. In this step, the taxpayer/business is required to create an invoice in the format defined in the e-invoice schema using the correct accounting software. Next, the supplier’s accounting software will generate one JSON for each B2B invoice. After this, the JSON file will be uploaded to the IRP.
Process 2: IRN Generation
The next step would be to generate a unique Invoice Reference Number (IRN) by the business/taxpayer using a standard hash-generation algorithm.
Process 3: Invoice Uploading
The next process is to upload the JSON file for each of the invoices with IRN to the Invoice Registration Portal, either directly or through third-party software.
Process 4: Authentication and Signing
In this process the authentication and signing process takes place. IRP will validate hashes / IRNs appended with JSON. If the file is not already uploaded by the taxpayer/business, it will generate an IRN and authenticate the file against the Central Registry of GST.
Once authenticated, it will add a signature on the invoice and a QR code on the JSON. As such, the already generated hash will become the new IRN of the e-invoice. This will be the unique identification of that e-invoice for the entire financial year.
Process 5: Sharing of Data
In this process, the uploaded data will be shared with the E-way bill and the GST system.
Process 6: E-invoice Downloading
In this process, e-invoice downloading takes place. The portal will send the digitally signed JSON file with IRN and QR code back to the taxpayer/business. Also, a copy of the invoice is sent to the taxpayer/business on their registered email id.
Applicability of GST E-invoice System
With the CBIC’s CGST announcement dated February 24, 2022, the e-invoicing system now applies to a wider range of firms. From April 1, businesses with a turnover of more than Rs 20 crore will be required to create electronic invoices for B2B transactions.
From April 1, 2022, additional vendors will be required to issue e-invoices. If the invoice is not valid, the recipient will not be able to claim the input tax credit and would be subject to penalties.
E-invoicing for business-to-business (B2B) transactions became essential under GST law on October 1, 2020, for businesses with over Rs 500 crore turnover. On January 1, 2021, for enterprises with over Rs 100 crore turnover.
Companies with more than Rs 50 crore turnover have been generating B2B e-invoices since April 1 last year. Companies having a turnover of more than Rs 20 crore are now eligible.
For Whom E-invoicing is Not Applicable?
The e-invoicing system will cover only business-to-business (B2B) transactions. The scope of the law excludes all financial organizations in the insurance and banking industries.
Non-banking financial enterprises, goods and passenger transportation agencies, business units operating in special economic zones, and government departments are also exempt from the system.
What are the consequences of forgetting to generate e-invoices?
It is regarded as an offence and penalized if an e-invoice is not produced.
Non-compliant businesses are subject to heavy fines of up to Rs.10,000 for each invoice. Furthermore, any incorrectly invoiced invoice maybe subject to a penalty of Rs.25,000.
Aside from the penalties, a taxpayer who delays the generation of an e-invoice may face the following consequences:
- GST returns aren’t being filled up automatically.
- Customers are unable to claim ITCs that are eligible.
- Customers will not accept invoices that do not follow the e-invoicing guidelines.
Features of e-invoice system you need to know
E-invoicing is a facility made available by the Government of India to establish an efficient GST processing system. Under this section of the blog, you will see the features of an e-invoicing system. It will clarify questions that arise under the new e-invoicing system.
Unique Invoice Reference Number (IRN)
Under the new e-invoicing system, the IRN can be defined as a unique number generated for invoices by the Invoice Registration Portal (IRP). Once a taxpayer uploads their software-generated invoice to the Invoice Registration Portal, a unique invoice reference number is generated by the system. This step ensures that the supplier does not submit the same document more than once within the financial year.
Digital Signature (DSC)
A digital signature is a method of electronically signing a document to authenticate that it has been submitted by the respective supplier.
Before the e-invoicing system, the GST rules required all invoices to be physically signed by the authorized individual. But after e-invoicing, an authorized individual could also affix their digital signature provided that they fulfilled the required provisions under the IT Act, 2000.
Quick Response Code (QR code)
QR code is helpful for tax officers checking the invoice. The IRP generates a QR code containing the unique IRN (hash) along with some important parameters of invoice and digital signature. It can be used to verify the invoices on the central portal as well as by an Offline App.
The QR code consists of the following e-invoice parameters:
- GSTIN of supplier
- GSTIN of Recipient
- Invoice number as given by Supplier
- Date of a generation of invoice
- Invoice value (taxable value and gross tax)
- A number of line items.
- HSN Code of the main item (the line item having the highest taxable value)
- Unique Invoice Reference Number (hash)
Get up and running with e-Invoicing in 1 minute Request a free demo
Documents to be communicated under e-invoicing
Many taxpayers are confused about the documents required for filing GST returns under e-invoicing. While filing GST, some more documents have to be submitted along with an e-invoice. These documents make it easy to complete tax filing for validating your e-invoice.
Following are the required documents to be submitted while filing the GST return-
- Supplier invoice
- Credit note by a supplier
- Credit note by a supplier
E-invoicing Template Mandatory Fields January 1, 2020
Here are the 50 mandatory fields of an e-invoice according to the e invoice sample notified previously –
| S.No. | Field name | Specifications/Choices/Sample Inputs | Remarks |
| 1. | IRN | Sample: 649b01 ft.Limit: 50 | An invoice contains a unique number. A seller can generate this number or leave it blank before submitting an invoice to IRP. If the seller generates an IRN, it will be validated by the system and registered for the invoice. An IRN can be generated with the e-invoice portal if the seller leaves this field blank. An IRN is important and it should be registered. |
| 2. | Invoice_Type_Code | Limit – 10Input can be one of these –Reg/SEZP/SEZWP/EXP/EXPWP/DEXP | Denotes SEZ supplies with payout, regular, SEZ supplies without payout, sale from the warehouse which is bonded, deemed exports, export with/without tax payment |
| 3. | Invoice No. | Limit: 16Sample input: ‘Sa/1/2019’ | Requires a sequential number for unique identification in the business time-frame, context, supplier records, and operating systems. No identification scheme must be there. |
| 4. | Date of Invoice | DD/MM/YYYY | Issuing date of invoice |
| 5. | Invoice_Period_Start_Date | DD/MM/YYYY | |
| 6. | Invoice_Period_End_Date | DD/MM/YYYY | |
| 7. | Preceding_Invoice_Reference | Limit: 16Input example:‘Sa/1/2019’ | Particulars of original invoice being changed by following document, including credit/debit note. You must have expansion of e-versions of debit notes/credit notes, and other documents needed under GST. |
| 8. | Preceding_Invoice_Date | DD/MM/YYYY | Date of issue of invoice |
| 9. | Supplier_Legal_Name | Limit:100 | Name given in supplier’s PAN |
| 10. | Supplier_GSTN | Alphanumeric numberLimit: 15 | Supplier’s GSTIN (who is drafting e-invoice) |
| 11. | Supplier_Address1 | Limit: 100 | Supplier’s address |
| 12. | Supplier_State | Limit: 50 | Supplier’s state |
| 13. | Supplier_Pincode | Limit: 6 | Supplier’s pincode |
| 14. | Billing_Name | Limit: 100 | Buyer’s trade name |
| 15. | Billing_GSTIN | Limit: 15 | Buyer’s GSTIN |
| 16. | Billing_POS | Limit: 02 | Supply state code |
| 17. | Billing_Address1 | Length: 100 | Buyer’s Locality/District/State on whom invoice has been billed/raised, if any |
| 18. | Billing_State | Length: 50 | Buyer’s state |
| 19. | Billing_Pincode | Length: 6 | Buyer’s pincode |
| 20. | Payee_Name | Limit: 100 | Person’s name to whom payment must be made |
| 21. | Payer_Financial_Account | Limit:18 | Payee’s account number |
| 22. | Payment mode | Limit: 6 | Credit/Cash/Transfer |
| 23. | Financial_Institution_Branch | Limit: 11 | IFSC code |
| 24. | Dispatch_From_Details | Dispatch location of the goods | |
| 25. | List | List of items and services billed | |
| 26. | Tax_Total | Decimal (10,2) | There are two instances of tax total required with the availability of tax currency code. |
| 27. | Paid_Amount | Decimal (10,2) | The advance payment of sum total. Rounded up to 2 decimals max. |
| 28. | Amount_due_for_payment | Decimal (10,2) | Outstanding amount that must be paid. Rounded up to 2 decimals. |
| 29. | Tax_Scheme | Limit: 4 | Important element. Usually consists of “GST” |
| 30. | Shipping_To_Name | Limit: 60 | Group of terms giving details about location where goods to be shipped |
| 31. | Shipping_To_GSTIN | Limit: 100 | Address where services and goods billed are or were delivered |
| 32. | ShippingTo_Address1 | Limit: 50 | Group of terms about the address where goods and services billed must be delivered. |
| 33. | ShippingTo_Pincode | Limit: 50 | Details about the address where services and goods to be delivered |
| 34. | ShippingTo_State | Limit: 100 | Details about the address where services and goods to be delivered |
| 35. | Subsupply Type | Limit: 2 | Details about the address where services and goods to be delivered |
| 36. | Transaction Mode | Limit: 2 | Details about the address where services and goods to be delivered |
| 37. | Company_Name | Limit: 60 | Individual and address to dispatch from |
| 38. | Address1 | Limit: 100 | Individual and address to dispatch from |
| 39. | State | Limit: 2 | Individual and address to dispatch from |
| 40. | Pincode | Limit: 6 | Individual and address to dispatch from |
| 41. | SLNO | Integer | In a sequence of 1,2,3 and so on… |
| 42. | Quantity | Decimal (13,3) | Number of items (services or goods) charged |
| 43. | Rate | Decimal (10,2) | No. of units on which price is applicable |
| 44. | Assessable Value | Decimal (13,2) | Unit price, excluding GST, before deducting discount on item price (shouldn’t be minus) |
| 45. | GST Rate | Decimal (3,2) | Rate of GST, given as percentage applicable to the billed item |
| 46. | Iamt | Decimal (11,2) | Amount of IGST according to the item |
| 47. | Camt | Decimal (11,2) | Amount of CGST as per the item |
| 48. | Samt | Decimal (11,2) | SGST as per the given item |
| 49. | Total value of invoice | Decimal (11,2) | Total GST to be charged on invoice. |
| 50. | Batch Name | Limit: 20 | Details of batch number for specific set of brands |
Mandatory E-invoicing format fields with a due date of July 30, 2020
Here are the 30 mandatory fields needed according to the recent format issued in July 2020 –
| Sl. no. | Name of the field | List of Choices/ Specifications/Sample Inputs | Remarks |
| 1 | Document Type Code | Enumerated List such as INV/CRN/DBN | Document type |
| 2 | Supplier_Legal Name | String Max length: 100 | Supplier’s Legal name who is raising the invoice |
| 3 | Supplier_GSTIN | Max length: 15 Must be alphanumeric | Supplier’s GSTIN who is raising the invoice |
| 4 | Supplier_Address | Max length: 100 | Supplier’s Building/Flat no., Road/Street, Locality, etc. who is raising the e-invoice |
| 5 | Supplier_Place | Max length: 50 | Supplier’s location such as city/town/village*mandatory |
| 6 | Supplier_State_Code | Enumerated list of states | Select the state from the recent list provided by GSTN |
| 7 | Supplier Pincode | Six digit code | Supplier’s locality/district/state |
| 8 | Document Number | Max length: 16 Sample can be “ Sa/1/2019” | A sequential number must be given for verifying the invoice in the business time-frame, context, supplier records and operating systems. No identification scheme can be used. |
| 9 | Preceeding_Invoice_Reference and date | Max length:16 Sample input is “ Sa/1/2019” and “16/11/2020” | Original invoice details to be amended by a credit or debit note. |
| 10 | Document Date | String (DD/MM/YYYY) as per the technical field specification | Date of issuing the invoice. The format must be “YYYY-MM-DD” under explanatory notes. It requires further clarity. The date of start and end of the document period should be given too. |
| 11 | Recipient_ Legal Name | Max length: 100 | Buyer’s name according to the PAN |
| 12 | Recipient’s GSTIN | Max length: 15 | Buyer’s GSTIN |
| 13 | Recipient’s Address | Max length: 100 | Supplier’s Building/Flat no., Road/Street, Locality, etc. raising the e-invoice |
| 14 | Recipient’s State Code | Enumerated list | Select the state code of buyer’s address |
| 15 | Place_Of_Supply_State_ Code | Enumerated list of states | Select the state from the recent list issued by GSTN |
| 16 | Pincode | Six digit code | Declare the place (locality/district/state) of the buyer on whom the invoice is raised/ billed, if any |
| 17 | Recipient Place | Max length: 100 | Recipient’s location (City/Town/Village) |
| 18 | IRN- Invoice Reference Number | Max length: 64 Sample is ‘a5c12dca8 0e7433217…ba4013 750f2046f229’ | Suppliers can leave this field empty during registration request. GSTN then generates a unique number once an e-invoice is uploaded on the GSTN website. The supplier will receive an acknowledgement once the portal accepts the e-invoice successfully. E-invoice must display the IRN before use. |
| 19 | ShippingTo_GSTIN | Max length: 15 | Buyer’s GSTIN or the anyone getting the delivery of a specific item |
| 20 | Shipping To_State, Pincode and State code | Max length: 100 for state, 6 digit pincode and enumerated list for code | State including the place where services and goods billed are or were delivered |
| 21 | Dispatch From_ Name, Address, Place and Pincode | Max length: 100 each and 6 digit for pincode | Entity’s name, and city/town/village dispatching the goods |
| 22 | Is_Service | String (Length: 1) by selecting Y/N | Whether or not service supply must be given |
| 23 | Supply Type Code | Enumerated list of codes Sample values can be either of B2B/B2C/ SEZWP/S EZWOP/E XP WP/EXP WOP/DE XP | To identify the supply type, such as B2C, B2B, supply to Exports/SEZ with/without giving payment and export deemed. |
| 24 | Item Description | Max length: 300 “Mobile” is the sample value. The “Identification scheme identifier of the product classification identifier” is the schema document.The sample value is ‘Mobile’ The schema document refers to this as the ‘identification scheme identifier of the Item classification identifier’ | Simply put, the relevant description generally used for the item in the trade. However, more clarity is needed on how it needs to be described for every two or more items belonging to the same HSN code |
| 25 | HSN Code | Max length: 8 | The applicable HSN code for particular goods/service must be entered |
| 26 | Item_Price | Decimal (12,3) Sample value is ‘50’ | The unit price, exclusive of GST, before subtracting item price discount, can not be negative |
| 27 | Assessable Value | Decimal (13,2) Sample value is ‘5000’ | The price of an item, exclusive of GST, after subtracting item price discount. Hence, Gross price (-) Discount = Net price item, if any cash discount is provided at the time of sale |
| 28 | GST Rate | Decimal (3,2) Sample value is ‘5’ | The GST rate represented as a percentage that is applicable to the item being invoiced |
| 29 | IGST Value, CGST Value and SGST Value Separately | Decimal (11,2) Sample value is ‘650.00’ | For each individual item, IGST, CGST and SGST amounts have to be specified |
| 30 | Total Invoice Value | Decimal (11,2) | The total amount of the Invoice with GST. Must be rounded to a maximum of 2 decimals |
Laser E-Invoice Bill Format with QR Code
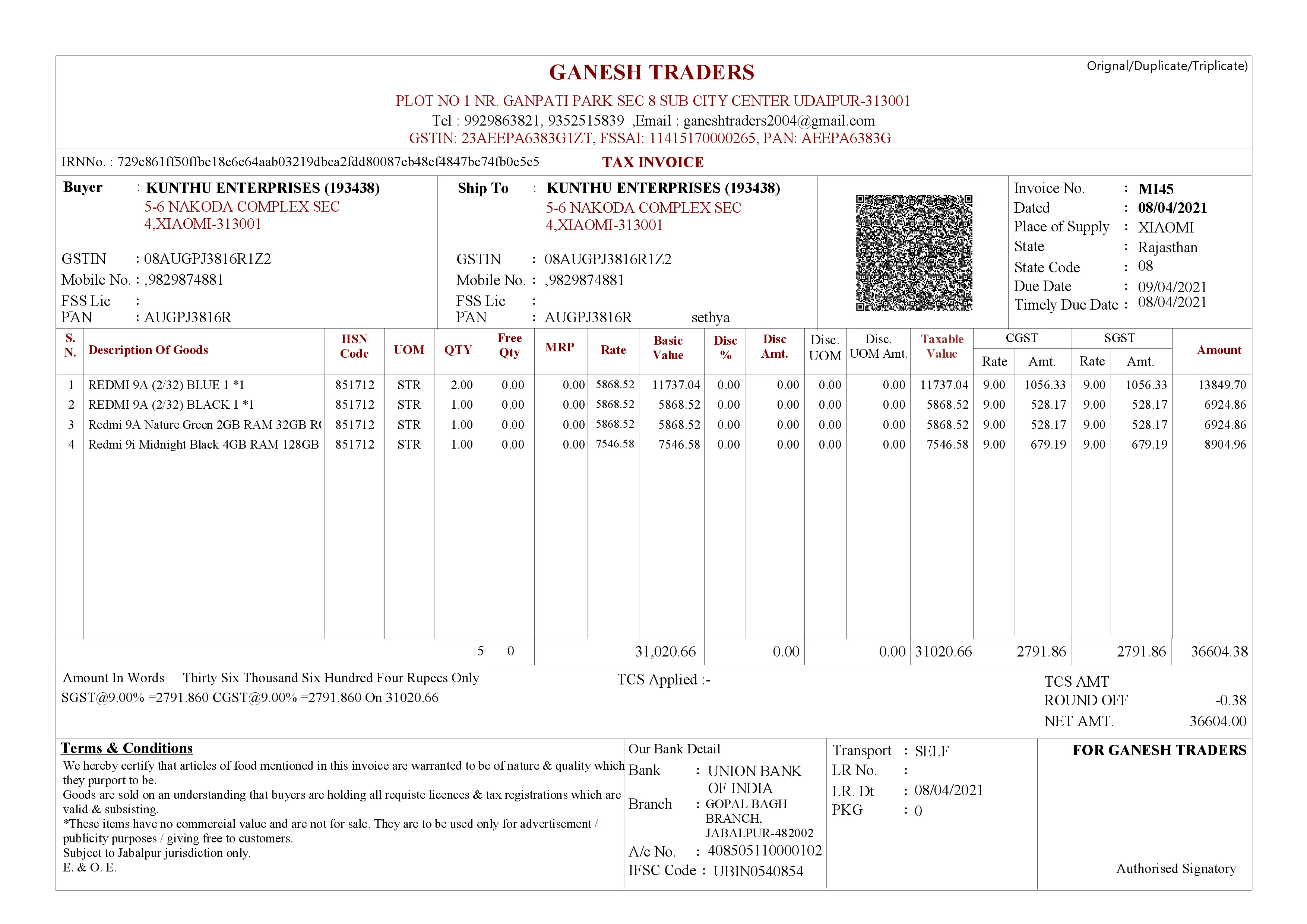
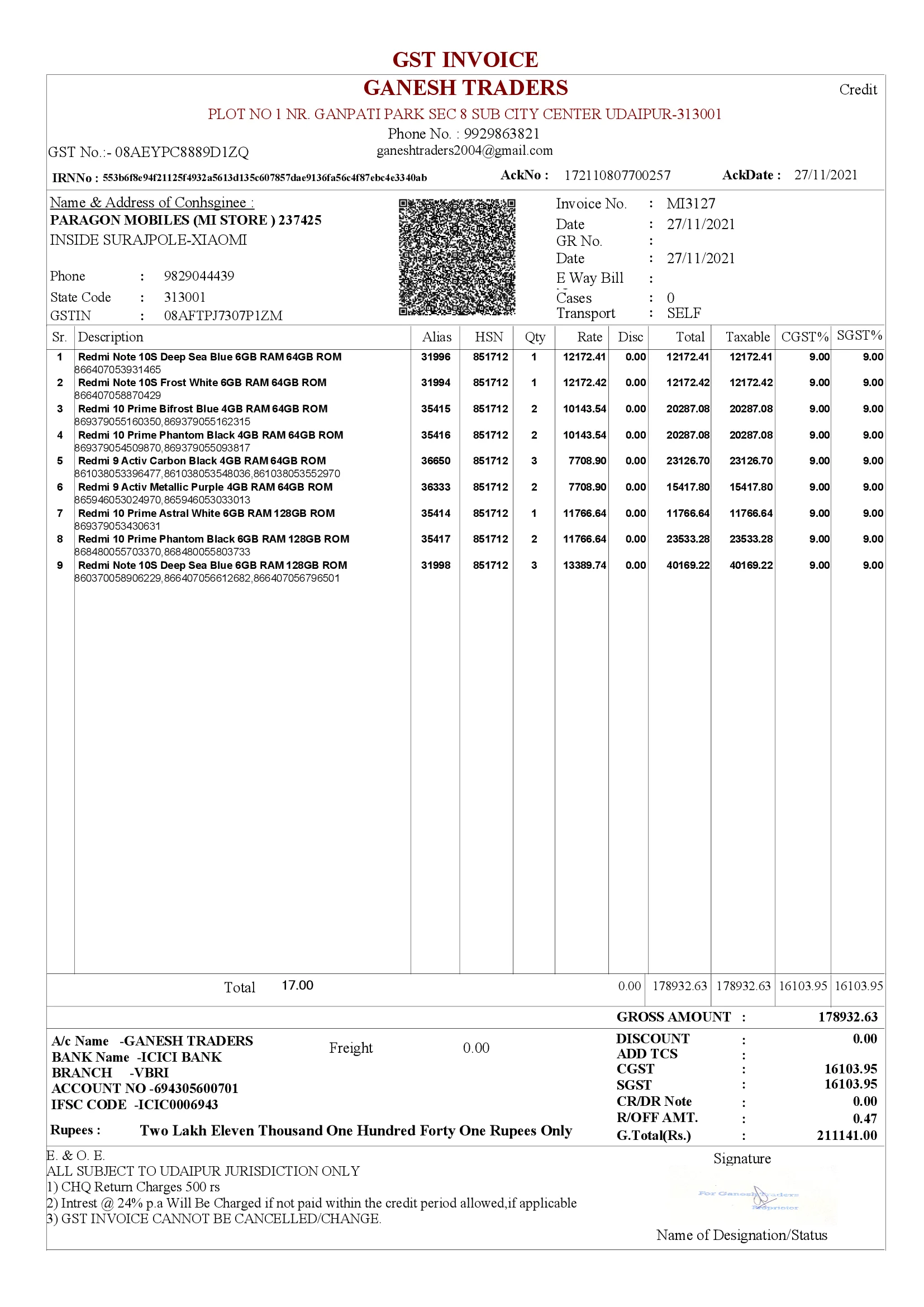
Benefits of e-invoicing system
E-invoicing benefits all suppliers, buyers, and the government. Adapting to an e-invoice system encourages system automation and makes taxation an efficient and time-saving process.
After the notification is passed for invoicing, businesses will now have to integrate their system with the government’s Invoice Registration Portal (IRP) for a smooth generation of Invoice Reference Numbers (IRN) for each B2B bill. Thus, businesses must get their accounting software to accommodate changes to comply with the e-invoicing schema.
At the same time, it gives businesses freedom from multiple data entry but also saves time by using the same data in different segments of taxation. This way, it offers-
- Fewer disputes
- Better account reconciliation
- Better account reconciliation
Benefits to Suppliers
- Faster payment and improved cash flow
- Better account reconciliation
- Reduced operational costs
- Fewer disputes and rejected invoices
- Improved customer satisfaction
Benefits to Buyers
- Increased productivity and automation
- Reduced costs
- Take advantage of early payment discounts
- Improved supplier relationship
Benefits to the Government
E-invoicing allows the government to completely track all the B2B invoices which will reduce the fraudulent invoices submitted to claim input tax credit. With e-invoicing, the government keeps all the records and can easily conduct the Tax liability check. The primary aim of the e-invoice is to verify the Tax evasion and fraudulent invoices submission.
Direct Invoice Generation
E-invoice is not generated from a government tax portal. It is implemented to ensure that the invoices will be generated, in a particular standard format by taxpayers by their own accounting or billing software. Taxpayers must follow the standard format for invoice generation which can be easily read by another system. If the details are in a proper format, it will improve the process of filing returns.
Invoice Registration Portal is made to record the details of the invoices only and not to generate the e- invoices.
GSTN has provided eight free accounting or billing software that assists you to generate JSON of the invoice you can also use other software which provides the same functions.
- Reduce the number of fraudulent invoices submission
- The government will be able to conduct system level matching of input credit and output tax
- Reduction in losses due to tax fraud
- Increase in productivity in tax administration
Benefits of e-invoicing to Taxpayers
No Multiple Entries:
With the help of e-invoicing, there is no need to enter multiple entries by buyer and seller. E-invoicing data is directly sent to the buyer and seller account once they start generating e-invoicing which will also help in to reduce reporting timing in multiple formats.
For Better Reconciliation:
As the data from e-invoicing is sent to the buyer, the buyer can reconcile with order and accept or reject it on a real-time basis.
For Less Error or avoid Duplication:
E-invoicing will decrease the issues of input credit and avoid the change of bill duplication with the help of Invoice Reference Number which is unique to each invoice.
Data not limited to GSTR-1
E-invoice will eliminate multiple entries while filing GSTR-1 and can use the same data for issuing e-way bills, and one can also use the same data while filing ANX-1 viz. sales and ANX-2 viz. purchase register.
Less fake invoices
In the e-invoicing process all invoices validate through the government portal and send automatically to buyers and sellers in real-time that reduces the chance of generating fake invoices.
Generating e-invoices will impact the business processes as follows-
- For compliance, the company must now identify transactions that are subject to e-invoicing.
- For accuracy, supplier and customer master data must be updated to incorporate extra invoice information such as GSTIN, bank account, and payee information.
- Businesses will need to adjust their GST return filing method since B2B supplies will be auto-populated in the returns while B2C supplies would need to be manually updated.
- Businesses must choose whether to comply with e-invoicing via API integration, offline utilities, or via GST Suvidha Provider (GSP).
- The most significant challenge that enterprises may encounter is engaging in real-time generation and IRN capture.
Businesses will get benefit from e-invoices in the following ways:
- E-Invoice overcomes and fills a crucial gap in data reconciliation under GST to eliminate mismatch errors.
- Interoperability and reduced data input mistakes are possible because another may read e-Invoices created with one piece of software.
- E-invoice allows you to track your supplier’s invoices in real-time.
- Backward integration and automation of the tax return filing process — invoice data would be auto-populated in different returns, especially when preparing part-A of e-way bills.
- Genuine input tax credits are becoming increasingly accessible.
- There is a lesser possibility of tax audits/surveys since the information necessary by the tax authorities is available at the transaction level.
Details of the official website for e-invoice generation
A taxpayer can use the following common GST Electronic Portals for the preparation of the E-invoice in terms of rule 48(4):
- einvoice1.gst.gov.in
- einvoice2.gst.gov.in
- einvoice2.gst.gov.in
- einvoice4.gst.gov.in
- einvoice5.gst.gov.in
- einvoice6.gst.gov.in
- einvoice7.gst.gov.in
- einvoice8.gst.gov.in
- einvoice9.gst.gov.in
- einvoice10.gst.gov.in
How will the e-invoicing system help businesses in the long run under GST?
E-invoice is very beneficial for the government as well as taxpayers. It provides a push towards a digital economy. Let’s take a look at the benefits of e-invoice under GST.
- The e-invoice system fills the gaps in data reconciliation under GST and reduces mismatch errors.
- The e-invoice system enables real-time invoice tracking.
- E-invoice encourages the availability of valid input tax credit.
- The e-invoice system provides pre-verification, which leads to fewer disputes.
- E-invoice, which is generated on particular software can be interpreted by some others.
- E-way bills can be auto-generated using e-invoice data.
- E-way bills can be auto-generated using e-invoice data.
Role of e-invoicing in small, medium, and big enterprises
In today’s digital age, we are constantly moving towards digitization. We are dropping the manual working process and moving towards automation to avoid loss in business. Electronic invoicing or e-invoicing is now a part of major business processes and is acceptable by businesses.
For large enterprises, it is affordable, but for small and medium-sized businesses, it is difficult to understand or very expensive to implement. But it facilitates trading with many useful features that give a business of all sizes a smart way of doing business and paying taxes. It offers businesses with-
- Facilitate Smart working process
- Facilitate Smart working process
- Help in error reduction
- Provide a visible audit trail
- Provide a visible audit trail
Modes of Registering for e-invoicing
API-based Registration:
In this mode, large business and accounting software interact and share the relevant JSON and get Invoice Registration Number through their software, it validates and generates one IRN request at a time, so it can be used in bulk requirements like the E-Way Bill generation system.
Web-based Registration:
In this mode, once the business generates an e-invoice invoice can be uploaded onto the Invoice Registration Portal for validating or generating the Invoice Reference Number.
Web IRP: National Informatics Centre (NIC)
Mobile-based Registration:
In this mode, IRP will provide a Mobile App so taxpayers can process the invoice
SMS-based Registration:
In this mode, Taxpayers can enter invoice details in a specific format and send it to the Invoice Registration Portal via SMS for validating and processing.
Offline tool-based Registration:
This GSTN will provide an offline tool to where you can enter the invoice date and generate the JSON file which can be uploaded in Invoice Registration Portal.
GST Suvidha Provider-based Registration:
In this Taxpayers consult with GST Suvidha Providers to get registered and help with compliance in reference to e-invoice.
SWIL GST Solution: Easiest Software Option to Handle E-Invoice
All taxpayers must file the invoice electronically on the IRP under the e-invoicing system. Businesses who were informed during India’s fourth phase of e-invoicing must take specific actions to ensure a seamless transition to e-invoicing.
Businesses should get involved with accounting software solutions with GST filling capability. Also, the ERP/Accounting system should be well configured for IRN generation to communicate smoothly with the IRP.
The software provides data security, which is crucial. E-invoices will usually be directly obtained from the accounting software.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is there a provision to amend the e-invoice?
Yes, a taxpayer can amend the e-invoice, which can only be done on the GSTN portal.
Can an e-invoice be partially/completely cancelled?
An e-invoice can only be fully cancelled. It cannot be partially cancelled. It must be submitted to the IRN within 24 hours of cancellation.
Will it be possible to upload invoices in bulk for the generation of IRN?
No, you must upload invoices into the IRP one at a time. A company’s ERP must be set up to accept requests for the upload of certain invoices.
What types of documents must be reported to the IRP?
Supplier invoice
Credit note by a supplier
Debit note by a supplier
Will the common GST portal have a feature for creating electronic invoices
No, the individual ERP software now used by businesses creates invoices. The invoice must follow the required specifications and follow the standard e-invoicing format.
Wrapping Up
GST e-invoicing is an enhancement of the GST structure. The purpose behind it is to channelized the way of reporting business to business (B2B) supplies to the GST system.
With the adoption of e-invoicing standard allows the authorities to stop unnecessary data breaches and errors. Moreover, GST E-invoicing streamline the process of filing GST returns and reduces the manual working, and increases efficiency.
If you are looking for the best e-invoicing software with GST solutions, SWIL’s business solutions RetailGraph, Unisolve, and SwilERP are right choices. Check our video to know how RetailGraph handles & Generates E-Invoice smartly. Also, you can go for the video of Handling of E-Invoice in Unisolve. This way, you will better understand how SWIL eases the business working.








